
The second is that when muscles are damaged, specific cells called satellite cells are activated that can connect to form new muscle filaments. Initially, muscle fibers can be divided into at least two more common filaments. Hyperplasia occurs through two basic systems. The treatment of hyperplasia relies on benign prostatic hyperplasia, and the combination of alpha 1 receptor blockers and 5 alpha reductase inhibitors is effective. Endometrial hyperplasia is usually caused by too muchĮstrogen without progesterone. An example of a typical proliferative response is the development and enlargement of glandular cells, which drain milk into the breast in response to pregnancy and plan future breasts accordingly. Hyperplasia can occur in specific tissues. Hyperplasia can be caused by a variety of reasons, including the proliferation of the basal layer of the epidermis to compensate for the misfortune of the skin, continuous irritation, hormonal dysfunction, or compensation for injury or infection. The consequences of pathological hyperplasia can provide a suitable basis for the development of tumor This is different from neoplasia, in which genetically abnormal cells manage to proliferate unphysiologically and do not respond to normal stimuli. Similar to physiological hyperplasia, cells that undergo pathological hyperplasia are controlled by growth hormone, if these stimuli are removed, the cells will stop proliferating.
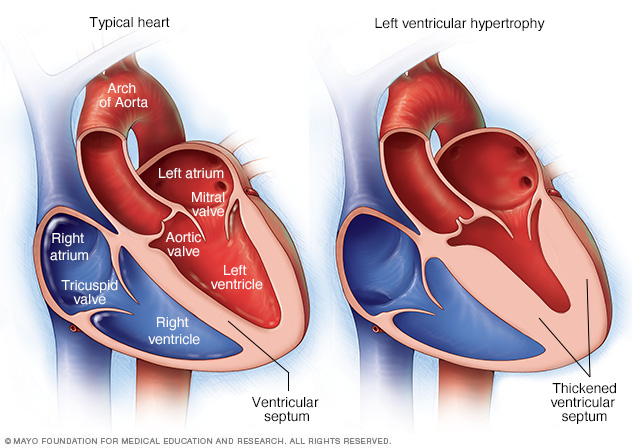
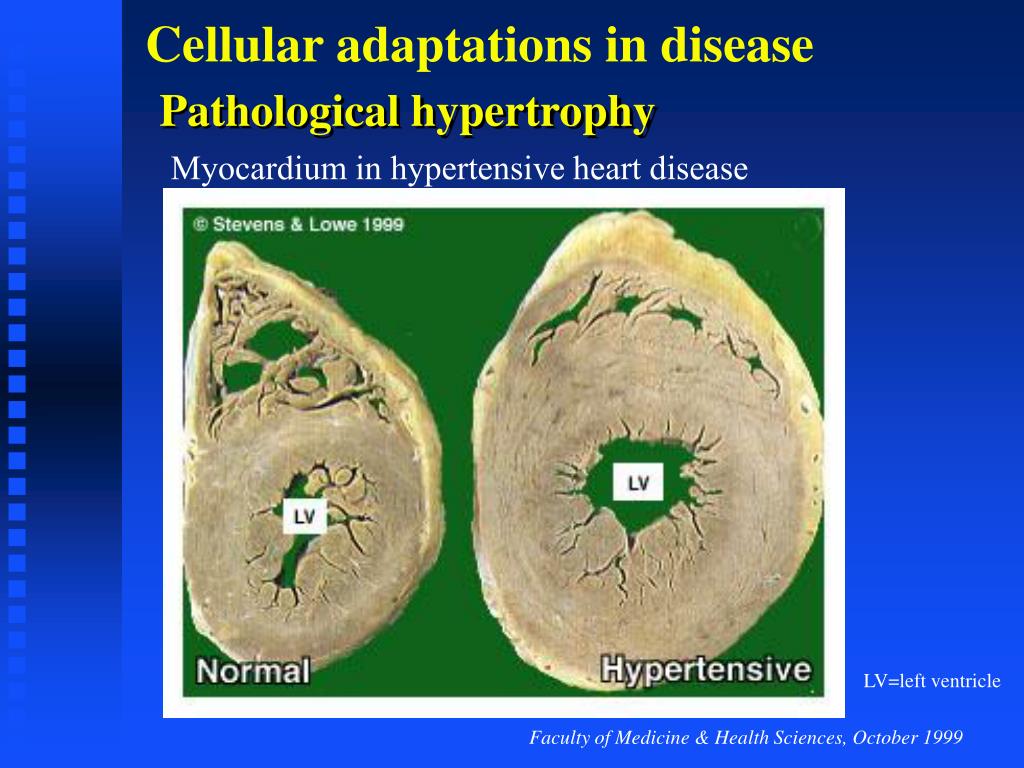
However, if excessive hormones or growth factors cause irritation, hyperplasia can occur as a pathological response. Hyperplasia is seen as a physiological response to a specific stimulus, and proliferating cells are still affected by normal regulatory control mechanisms. An example of a normal proliferative response is the milk-secreting gland cells in the breast that grow and multiply after pregnancy to prepare for future breastfeeding. Hyperplasia may be harmless and occur in certain tissues. The adaptive cell change of hypertrophy is an increase in cell size, while hyperplasia involves an increase in the number of cells. Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy. These cells look like normal cells, but their numbers have increased. Hyperplasia is a common response to stimuli. It can cause significant enlargement of organs. Heart: The heart can increase in size as a result of physical exercise, long-standing high blood pressure, obstruction to blood flow out of the heart, or genetic conditions that affect the growth of muscle cells in the heart.Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of organic tissues causedīy cell proliferation.This allows the uterus to grow along with the developing baby. Uterus: The muscles in the uterus undergo hypertrophy during pregnancy.This makes the muscles stronger and better able to handle physical stress. Muscles: Physical exercise leads to skeletal muscle hypertrophy.Hypertrophy is described as pathologic when it is caused by disease or leads to impaired function. Hypertrophy is described as physiologic when it helps or improves the way the organ or tissue functions. During pregnancy, the muscle cells in the uterus undergo hypertrophy in response to increased hormone stimulation. Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells commonly undergo hypertrophy in response to increased physical demand and stress on the cells. In contrast to hyperplasia, hypertrophy does not result in an increased number of cells. Another word for hypertrophy is hypertrophic. Hypertrophy is an increase in the size of cells that leads to an overall increase in the size of the tissue or organ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
